RFID Dry inlay does not contain back glue, and its structure is antenna + chip + chip package;
RFID Wet inlay contains back glue, which can be directly attached to objects. The structure is antenna + chip + chip package + PET + Glue+ Release paper
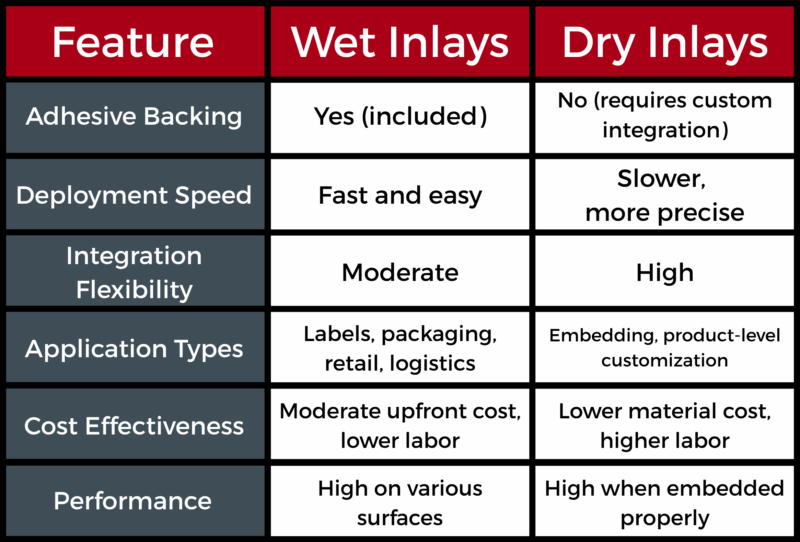
Choosing between a wet inlay and a dry inlay hinges on key application factors:
If you require instant adhesion to a surface, an RFID wet inlay with adhesive backing provides a ready-to-use solution. This is especially useful for labels, packaging, or tags used in inventory or logistics operations.
Dry inlays offer greater customization for embedding within specific materials, while wet inlays are easier to apply directly. For streamlined manufacturing, a wet RFID inlay is often preferable.
Environments exposed to moisture or temperature fluctuations may benefit from wet inlays because of their secure adhesion and excellent performance on various surfaces.
When deployment speed is critical—like in large-scale inventory management or supply chain rollouts—a wet RFID inlay ensures fast and efficient application.
While wet inlays may come with slightly higher initial costs due to the adhesive layer, they reduce labor time. Dry inlays, though more labor-intensive, can offer cost effectiveness in high-volume or embedded applications.
Both RFID wet inlays and dry inlays are used in a wide array of industries, including:



Copyright © ©Copyright 2024 Greatest IoT Technology Co., Ltd all rights reserved - Privacy policy